Numa
Numa
Это заготовка статьи про Numa
cat /sys/class/net/enp6s0f0/device/numa_node
Можно ли использовать один CPU в многопроцессорных системах? (и почему)
Почему возникает такой вопрос?
По-тому что системы с 2 и более сокетами на материнской плате допускают возможное расширение без полной замены сервера
Ответ на вопрос - "Да, работать будет", но с некоторыми оговорками.
Пояснение
Supermicro X8DTN
Подавляющее большинство материнских плат «просто работают»,
если вы поставить процессор в сокет с наименьшим номером
Это справедливо как для материнских плат Intel, так и для AMD в целом, а в случае сомнения информацию можнонайти в руководстве (но у меня никогда таких сомнений не было)
Вот пример материнской платы Supermicro X8DTN, которая представляла собой довольно двухпроцессорную плату Xeon серий Intel 5500 и 5600.
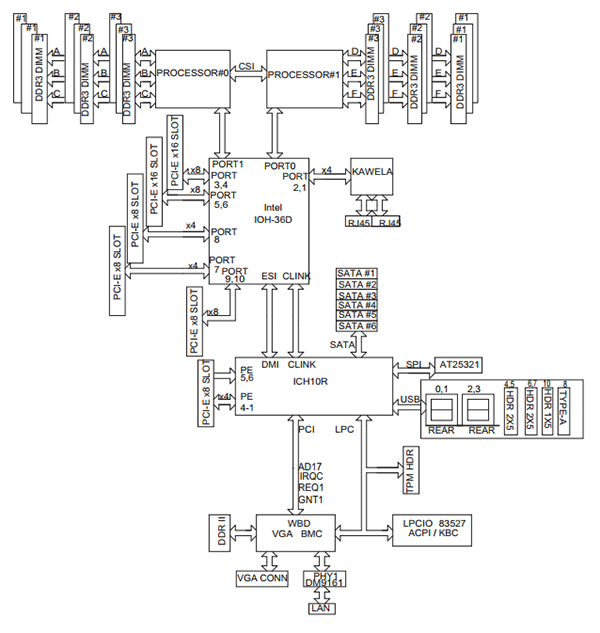
Since the Intel 5500 and 5520 series chipset had an IOH northbridge, populating only one CPU slot in the dual socket motherboard did not cut out any additional motherboard resources. In the Intel socket LGA1366 days, and with the AMD C32 and G34 platforms, both the northbridge and southbridge were found on the motherboard so the CPUs generally connected through the northbridge to get to an expansion card bus. In these systems, the main impact of only having one CPU (other than the obvious loss in CPU performance without the second CPU) is that one could not populate the memory banks for the empty processor slot. This is very similar to the single CPU nodes we use for the STH colocation project, even though each Dell C6100 node is dual processor capable.
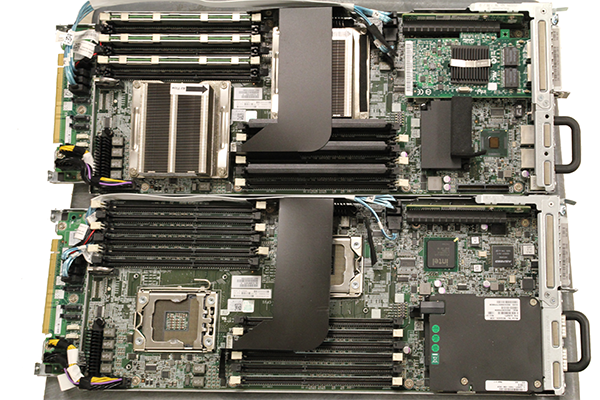

Underneath those heatsinks on the upper node sits only one processor despite the board being dual-processor capable. One can also see that the associated DRAM bank is filled with DDR3 RDIMMs while the empty socket is utilizing DIMM blanks. This setup is much different than a more modern LGA2011 dual Intel Xeon motherboard. Here is an example of a Supermicro X9DRH-7TF which has both onboard LSI SAS and Intel X540 10GbE:
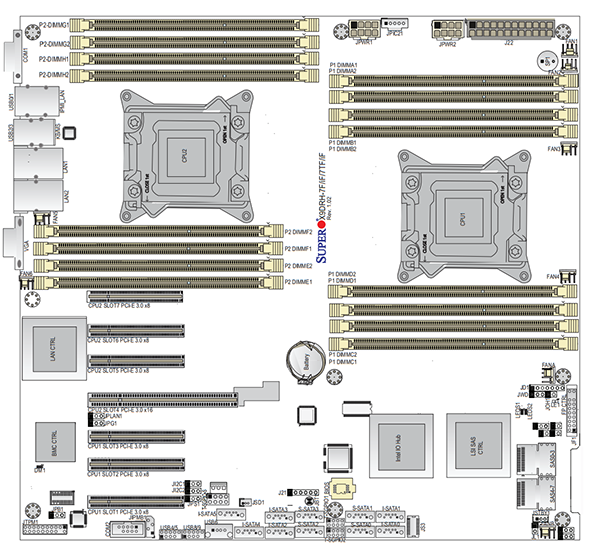
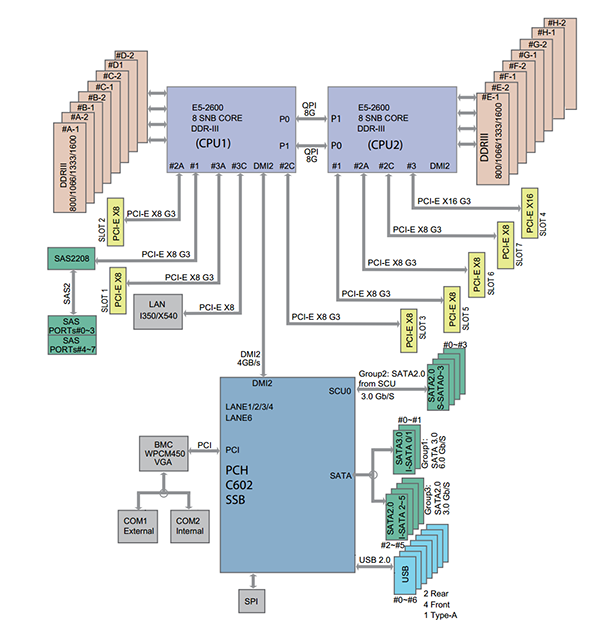
Today’s architectures add another level of complexity. With the dual Intel Xeon E5 LGA2011 platform as an example, the PCIe expansion slots are directly tied to a CPU. On the picture above, one can see each PCIe slot tied to a specific CPU. When a CPU socket is not populated, the PCIe lanes do not terminate. This has a major impact on the functionality of the motherboard. For example, if the second CPU socket is not filled in a dual socket motherboard oftentimes onboard devices such as Ethernet and SAS controllers may not work. Furthermore, PCIe lanes may not work. This will render the slots useless until the additional CPU(s) are added. Here is an associated diagram for the Supermicro X9DRH-7TF:
Here we can see that if CPU1 was missing, the onboard Intel X540 10GbE LAN and LSI SAS2208 controller do not have a PCIe but to hang off of. Conversely, with no CPU2, one would not have access to several PCIe 3.0 x8 slots. Luckily, most motherboard manufacturers state in their manuals which socket to populate.